Taeho Jo, Jie Hou, Jesse Eickholt & Jianlin Cheng, Scientific Reports (2015)
The three–dimensional structure of Heterosigma akashiwo Na+–ATPase (HANA) was predicted by means of homology modeling based on the crystal structure of the K+–bound form of shark Na+/K+–ATPase (PDB ID: 2ZXE). The overall structure of HANA appears to be similar to that of shark Na+/K+–ATPase. Both contain three characteristic cytoplasmic domains, A, N and P, which are unique to P–type ATPases. HANA has a long TM7–8 junction as a large extracellular domain, in place of the β–subunit of shark Na+/K+–ATPase. Two putative K+–binding sites in the transmembrane domain of HANA were identified by means of valence mapping based on the constructed structure. The presence of K+–binding sites and the reported ion requirements for ATPase activity and EP formation indicate that HANA may transport K+ ions in the same manner as animal Na+/K+–ATPases.
Evaluation of Protein Structural Models Using Random Forests
Renzhi Cao, Taeho Jo, Jianlin Cheng, arXiv (2016) We propose a new protein quality assessment method which can predict both local and global quality of the protein 3D structural models. Our method uses both multi and single model quality assessment method for global quality assessment, and uses chemical, physical, geo-metrical features, and global quality score for local quality assessment. CASP9 targets are used to generate the features for local quality assessment. We evaluate the performance of our local quality assessment method on CASP10, which is comparable with two stage-of-art QA methods based on the average absolute distance between the real and predicted distance. We blindly tested our method on CASP11, and the good performance shows that combining single and multiple model quality assessment method could be a good way to improve the accuracy of model quality assessment.
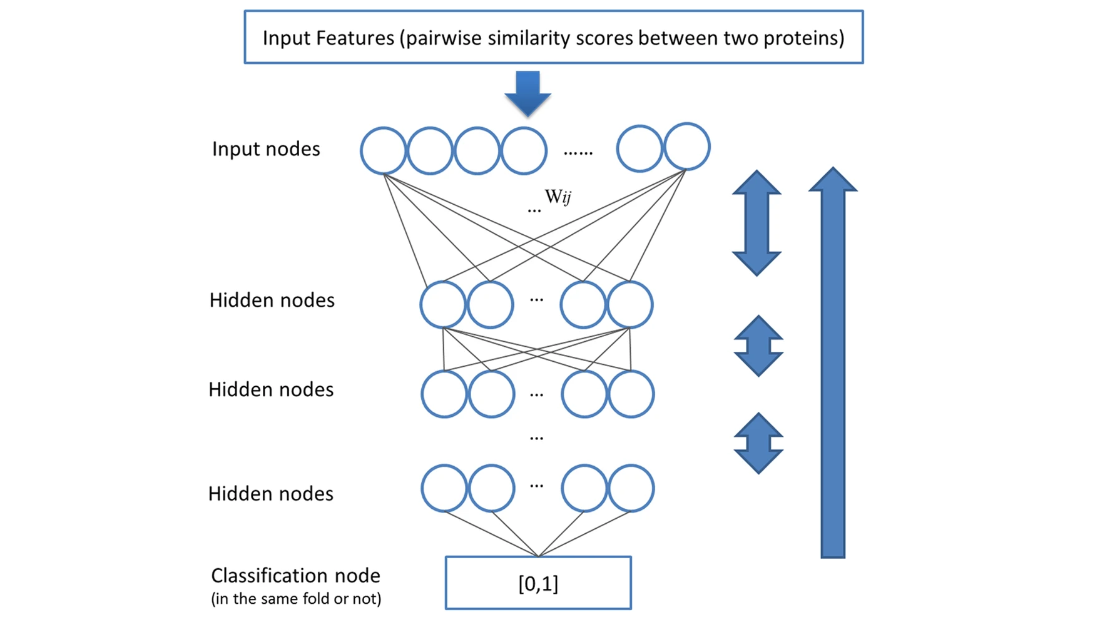
Improving Protein Fold Recognition by Deep Learning Networks
Taeho Jo, Jie Hou, Jesse Eickholt & Jianlin Cheng, Scientific Reports (2015) The three–dimensional structure of Heterosigma akashiwo Na+–ATPase (HANA) was predicted by means of homology modeling based on the crystal structure of the K+–bound form of shark Na+/K+–ATPase (PDB ID: 2ZXE). The overall structure of HANA appears to be similar to that of shark Na+/K+–ATPase. Both contain three characteristic cytoplasmic domains, A, N and P, which are unique to P–type ATPases. HANA has a long TM7–8 junction as a large extracellular domain, in place of the β–subunit of shark Na+/K+–ATPase. Two putative K+–binding sites in the transmembrane domain of HANA were identified by means of valence mapping based on the constructed structure. The presence of K+–binding sites and the reported ion requirements for ATPase activity and EP formation indicate that HANA may transport K+ ions in the same manner as animal Na+/K+–ATPas...
Improving protein fold recognition by random forest
Taeho Jo & Jianlin Cheng, BMC Bioinformatics (2014) RF-Fold consists of hundreds of decision trees that can be trained efficiently on very large datasets to make accurate predictions on a highly imbalanced dataset. We evaluated RF-Fold on the standard Lindahl's benchmark dataset comprised of 976 × 975 target-template protein pairs through cross-validation. Compared with 17 different fold recognition methods, the performance of RF-Fold is generally comparable to the best performance in fold recognition of different difficulty ranging from the easiest family level, the medium-hard superfamily level, and to the hardest fold level. Based on the top-one template protein ranked by RF-Fold, the correct recognition rate is 84.5%, 63.4%, and 40.8% at family, superfamily, and fold levels, respectively. Based on the top-five template protein folds ranked by RF-Fold, the correct recognition rate increases to 91.5%, 79.3% and 58.3% at family, superfamily, and fold levels.
Homology Modeling of an Algal Membrane Protein, Heterosigma Akashiwo Na^+-ATPase
Taeho Jo, Mariko Shono, Masato Wada, Sayaka Ito, Junko Nomoto, Yukichi Hara, Membrane (2010) The three–dimensional structure of Heterosigma akashiwo Na+–ATPase (HANA) was predicted by means of homology modeling based on the crystal structure of the K+–bound form of shark Na+/K+–ATPase (PDB ID: 2ZXE). The overall structure of HANA appears to be similar to that of shark Na+/K+–ATPase. Both contain three characteristic cytoplasmic domains, A, N and P, which are unique to P–type ATPases. HANA has a long TM7–8 junction as a large extracellular domain, in place of the β–subunit of shark Na+/K+–ATPase. Two putative K+–binding sites in the transmembrane domain of HANA were identified by means of valence mapping based on the constructed structure. The presence of K+–binding sites and the reported ion requirements for ATPase activity and EP formation indicate that HANA may transport K+ ions in the same manner as animal Na+/K+...
- 1




