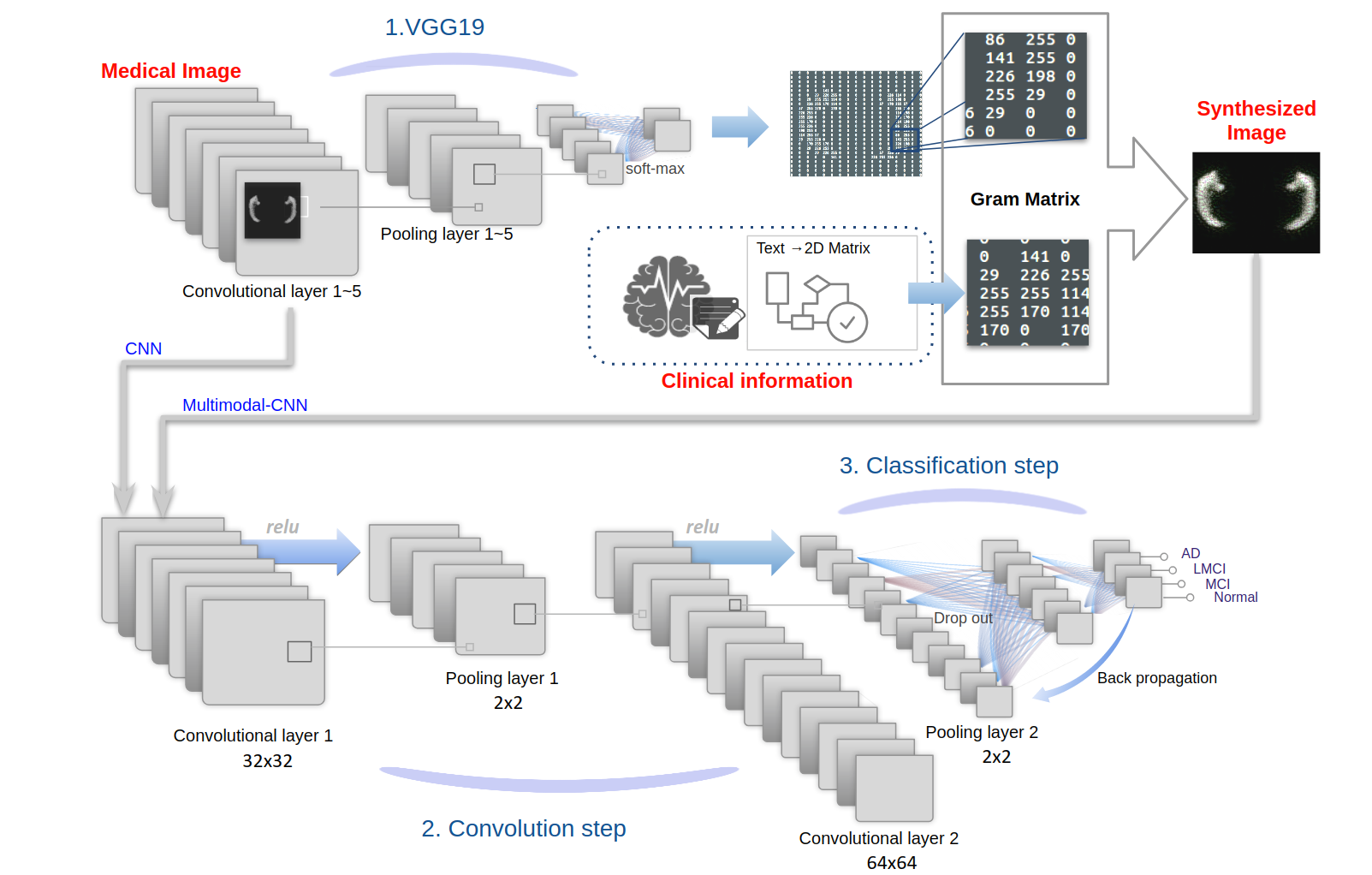
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Shannon L. Risacher, Jingwen Yan, Andrew J. Saykin, AAIC (2018)
Intermediate layers of the CNN were extracted, and the patient's clinical information was added by the gram matrix method. The clinical information was encoded as 2D matrices in this method, and the 2D images were extracted for train set by using the hippocampal segmentations, downloaded from the LONI ADNI site, carried out using Surgical Navigation Technologies (SNT). CNN with augmentation was performed on baseline scans from 103 participants with AD, 144 cognitively normal (CN) controls. Global CDR scores and the number of APOE ε4 alleles were included as clinical and genetic data.
Deep learning detection of informative features in tau PET for Alzheimer’s disease classification
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Shannon L. Risacher & Andrew J. Saykin for the Alzheimer’s Neuroimaging Initiative, BMC Bioinformatics (2020) We developed a deep learning-based framework to identify informative features for AD classification using tau positron emission tomography (PET) scans. The 3D convolutional neural network (CNN)-based classification model of AD from cognitively normal (CN) yielded an average accuracy of 90.8% based on five-fold cross-validation. The LRP model identified the brain regions in tau PET images that contributed most to the AD classification from CN.
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Shannon L. Risacher, Andrew J. Saykin, AAIC (2020) We downloaded 458 tau PET images (196 CN, 196 MCI, and 66 AD) from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and included only one scan per individual. SPM12 was used to process the tau PET data using standard techniques. We used a 3D convolution neural network (CNN) method for the classification, and applied a layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP) algorithm to identify informative features and to visualize the classification results. Five-fold cross validation was applied, where 70% of the entire data set was used for model training, 20% for model testing, and 10% for independent validation.
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Andrew J. Saykin, Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience (2019) The application of deep learning to early detection and automated classification of AD has recently gained considerable attention, as rapid progress in neuroimaging techniques has generated large-scale multimodal neuroimaging data. A systematic review of publications using deep learning and neuroimaging data for diagnostic classification of AD was performed. A PubMed and Google Scholar search was used to identify deep learning papers on AD published between Jan 2013 and July 2018. These papers were reviewed, evaluated, and classified by algorithm and neuroimaging type, and the findings were summarized.
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Shannon L. Risacher, Andrew J. Saykin, AAIC (2019) Demographic information, 3D MRI and PET image data, and APOE data were downloaded from the ADNI data repository (N=329; 185 CN and 144 AD). In our novel Multimodal-3DCNN approach, we first applied 3D Convolutional Neural Network (3D-CNN) to multimodal neuroimaging (MRI and PET) and then combined the output of 3D-CNN with APOE ε4 genotype and demographic information (age, sex, education, handedness etc.) using a gram matrix method (mCNN; Jo et al. AAIC2018). Finally, Deep Neural Network (DNN) was used to distinguish individuals with AD from CN. A 5-fold cross validation approach was employed to evaluate performance.
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Shannon L. Risacher, Jingwen Yan, Andrew J. Saykin, AAIC (2018) Intermediate layers of the CNN were extracted, and the patient's clinical information was added by the gram matrix method. The clinical information was encoded as 2D matrices in this method, and the 2D images were extracted for train set by using the hippocampal segmentations, downloaded from the LONI ADNI site, carried out using Surgical Navigation Technologies (SNT). CNN with augmentation was performed on baseline scans from 103 participants with AD, 144 cognitively normal (CN) controls. Global CDR scores and the number of APOE ε4 alleles were included as clinical and genetic data.
- 1





