Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Andrew J. Saykin, AAIC (2023)
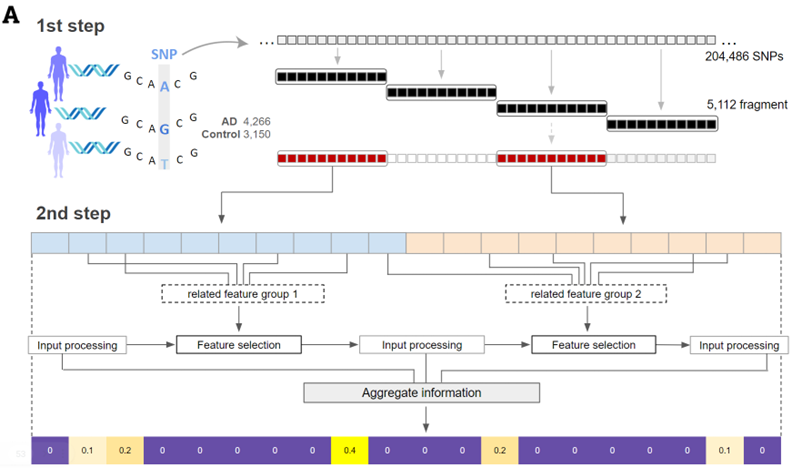
The study introduces SWAT-TAB, an evolved form of SWAT-CNN, optimized for identifying genetic variants in Alzheimer's disease (AD). It utilizes the Tabnet algorithm to meticulously select relevant features using a concept called sequential attention and was applied to ADSP WGS data, revealing pivotal genetic features. SWAT-TAB demonstrated enhanced efficiency, offering reduced processing time and improved ease of implementation compared to its predecessor.
LD‐informed deep learning for Alzheimer's gene loci detection using WGS data
Taeho Jo, Paula Bice, Kwangsik Nho, Andrew J. Saykin, the Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project, Alzheimer & Dementia TRCI (2025) Deep‐Block is a multi‐stage deep learning framework designed to detect AD associated genetic loci in large‐scale WGS data. It segments the genome based on linkage disequilibrium, applies sparse attention to select key blocks, and evaluates SNP feature importance with TabNet/RF. In a study of 7416 participants, 30,218 LD blocks were identified, including novel variants and established APOE loci. The results were supported by eQTL analysis across 13 brain regions and comparisons to existing GWAS data.
Deep Learning-based SWAT-Tab Approach for Identifying Genetic Variants using Whole Genome Sequencing
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Andrew J. Saykin, AAIC (2023) The study introduces SWAT-TAB, an evolved form of SWAT-CNN, optimized for identifying genetic variants in Alzheimer's disease (AD). It utilizes the Tabnet algorithm to meticulously select relevant features using a concept called sequential attention and was applied to ADSP WGS data, revealing pivotal genetic features. SWAT-TAB demonstrated enhanced efficiency, offering reduced processing time and improved ease of implementation compared to its predecessor.
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Paula Bice, Andrew J Saykin, For The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, Briefings in Bioinformatics (2022) We propose a novel three-step approach (SWAT-CNN) for identification of genetic variants using deep learning to identify phenotype-related single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that can be applied to develop accurate disease classification models. We tested our approach using GWAS data from the ADNI including (N = 981; CN = 650, AD = 331). Our approach identified the well-known APOE region as the most significant genetic locus for AD. Our classification model achieved an AUC of 0.82.
Deep learning–based genome-wide association analysis in Alzheimer’s disease
Taeho Jo, Kwangsik Nho, Andrew J. Saykin, AAIC (2021) We used genome-wide genotyping data (12,448,786 SNPs following imputation) from 916 participants in the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (458 cognitively normal controls and 458 AD patients). A convolutional neural network (CNN) consisting of convolutional, pooling and fully connected Softmax layers was used in a two-stage approach.
- 1




